The Hidden Side of Exocad: 6 Ways to Maximize Its Power
Exocad is undoubtedly one of the most powerful design software tools out there.
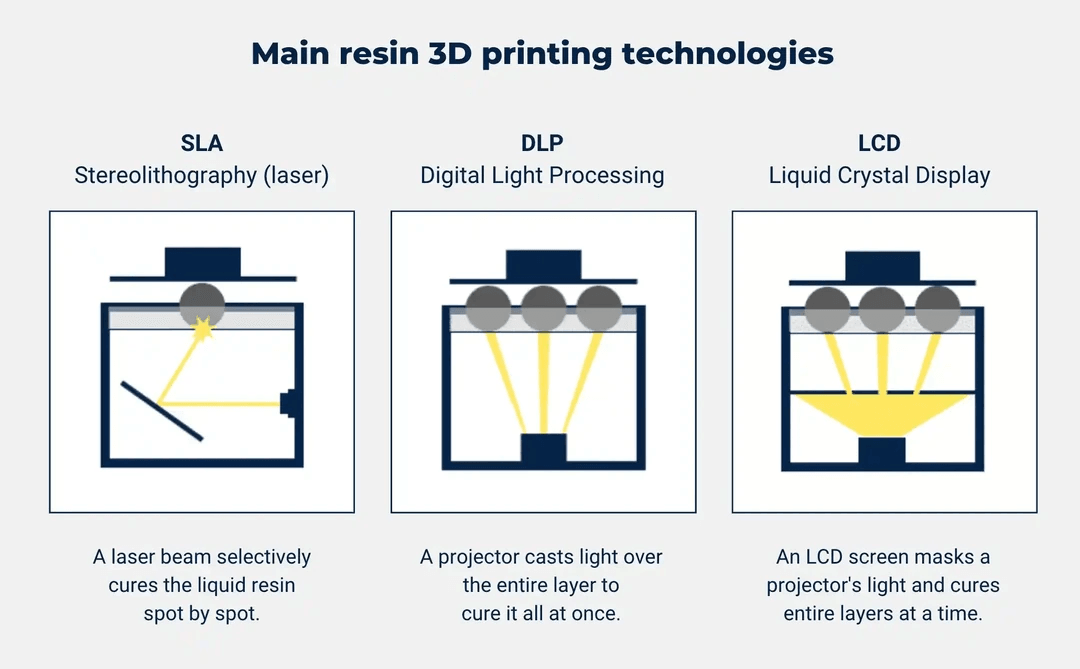
3D printing technologies are diversifying and improving in parallel with rapid developments in the industry. In this article, we will focus particularly on SLA (Stereolithography), DLP (Digital Light Processing), and LCD (Liquid Crystal Display) 3D printing technologies.
SLA (Stereolithography)
SLA is a 3D printing technology that works by solidifying resin with light. A laser solidifies the resin with the help of galvo mirrors. The platform is raised layer by layer according to the layer thickness and is repeated until the process is complete. The model remains in the resin print tank untouched by the laser and can be reused.
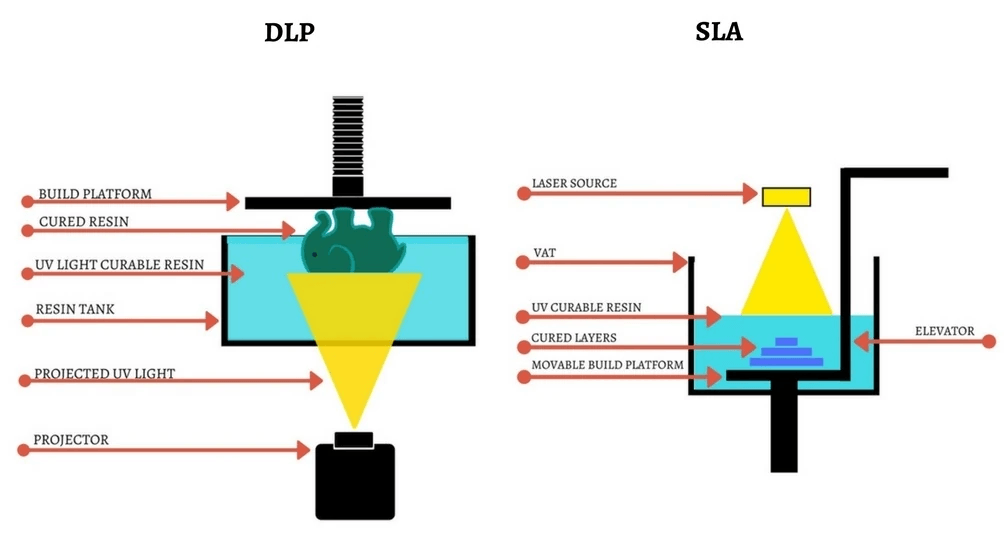
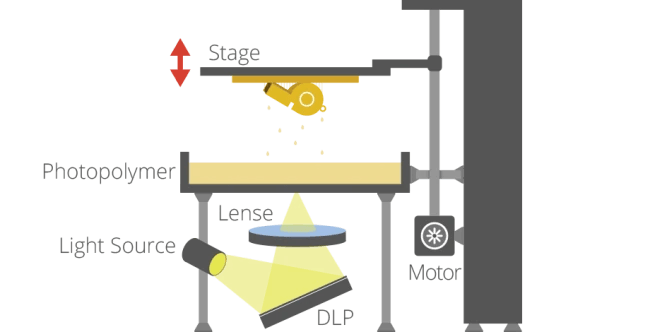
DLP (Digital Light Processing)
DLP is similar to SLA, but the light source is a projector. In DLP 3D printers, a digital projector screen with a single image is used. DLP ensures the solidification of the entire layer with a single flash. This technology offers the advantage of rapid production.
LCD (Liquid Crystal Display)
LCD 3D printers operate with a process similar to DLP, but they use LCD and LED as the light source. LCD printers, which are cost-effective, can provide high-quality prints and achieve various dimensional accuracies. LCDs can be replaced at low cost when their lifespan ends.